Creating pairs without duplication
You can create a list of every possible combination of two lists of items by performing a link and expand. However, with this method, you will get duplicate pairs, where the items are simply listed in a different order (i.e., reciprocals). Using computed columns and g_functions, you can create a list of pairs without any reciprocals.
Difficulty
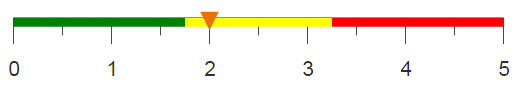
Objective
You want to compute the affinity of every pair of items bought together. To complete this analysis, you need to create the pairs within each basket from a transaction table. However, this table is already large, so performing a link and expand to create the pairs will create an even larger worksheet, as well as duplicate pairs. To avoid these inefficiencies, you should only expand the table as much as necessary to allow for the creation of all pairs of items without creating duplicates.
Solution
<block name="expand_prep"> <sel value="year(trans_date)=2016 & month(trans_date)=03"/> <sel value="g_first1(transid sku;;)"/> <willbe name="order" value="g_cumcnt(transid;;)"/> <willbe name="num" value="g_ucnt(transid;;sku)"/> <willbe name="expand" value="num-order"/> </block> <base table="pub.doc.retail.altseg.sales_detail_transid"/> <insert block="expand_prep"/> <sel value="expand" expand="1"/> <willbe name="linker" value="order+ii_(1)"/> <link table2="pub.doc.retail.altseg.sales_detail_transid" col="transid,linker" col2="transid,order"> <insert block="expand_prep"/> <colord cols="transid,sku,order"/> </link> <colord cols="transid,sku,c1"/>
Discussion
Before beginning any expansions, a selection is done on the table in order to limit the results to a specific time period. This will help prevent the table from becoming unnecessarily large. Additionally, only the first instance of each transaction/SKU is selected because if a specific item is bought twice in one transaction, you don't need to compare it to itself.
Now that the table is reduced to only the necessary data points, you can start creating the
preparatory columns for the expansion. First, you need a column that specifies the order of
products within each transaction. This can be done by performing a cumulative count for each
transaction. The order of the products is important because each product is expanded in
order to accommodate the products that appear after it, therefore a definitive order is
needed. Then, you need a column that indicates how many products are in each transaction,
which is calculated with g_ucnt(G;S;X). By subtracting the order of each
product from the number of products contained in the transaction, you can determine how many
times to expand each row.
Each item in the transaction will be expanded to accommodate the number of unique products that appear thereafter in the same transaction. Using this method, the first item will be expanded once for every item in the transaction excluding itself. The next item will be expanded one time less than the first and so on, until the last item is actually not expanded at all, but rather removed from the table, as it will have appeared in every prior pair.
Once the table is expanded, it is linked to itself using the linker column
and the order column. The column, linker, is created by
adding the enumeration of each SKU in each transaction to that SKU's order. For example, SKU
112741 in transaction
-2081370256 is expanded three times, and it's the first SKU
listed in the transaction. Therefore, in the linker column, the first
instance of the SKU will have a value of 2, (1+1), the second instance will
have a value of 3, (1+2), and the third instance will have a value of 4,
(1+3). Linking this column to the order column from the
same table, will create the unique pairs of items.
Common errors
- There was a problem getting a worksheet for a link (this can be caused by the worksheet being too large). The trapped error was: Too much data to get from table at subprocesses; hide some columns or select fewer rows
- If the table that you are working with is larger than 10,000,000 rows after the expansion, it will be too large to link to itself due to worksheet size limitations. In order to avoid this error, you can make further selections on your original table in order to decrease the worksheet size.
Further reading
If you would like to learn more about the functions and operations discussed in this recipe, click on the links below:
