Python in 1010data: Basic syntax
You can use Python to build query operations or ops in the 1010data Macro Language.
The <code> tag in Macro Language now supports the attribute
language_="python", allowing your analysis to contain Python code.
This means that table transformations, query operations, and metadata transformation can
now be done with Python. The Python code is run in the accum. See <code> in the 1010data
Reference Manual for more information about the <code>
tag.
When you invoke <code language_="python">, the platform automatically
imports numpy, pandas, sklearn, and
ten. numpy is imported as np and
pandas is imported as pd. ten is
a 1010data-supplied module that is loaded into the Python session. ten
is used to import data and metadata, get the number of rows, and set to temp tables or
worksheets.
On entering the Python session from <code>, the session automatically
gets the variables ops and table. ops
represents the current state of query operations in effect up to the
<code> tag. table is the base table, and will
normally be default.lonely. On exiting <code>, the
platform will examine the Python session for a variable named ops and
extract it. The new ops variable will now represent the current state
of the query. This allows the user to modify the query by modifying ops
or replace the query entirely with a completely new set of ops.
For example, the end of your Python code can use the rebase method in
ten and then set the value of ops as follows:
ops=ten.rebase(example_data_frame)The DataFrame
example_data_frame will then become a worksheet, and on exiting
<code>, the DataFrame will effectively become
the new state of the query.
When using the <code language_="python"> tag, it is good practice to
put the Python functions and related operations inside of a CDATA
tag.
Syntax
The basic syntax for Python language within 1010data Macro Language is as follows:
<code language_="python">
<![CDATA[python code]]>
</code>Example
The following is a simple example of the Python language within the Macro Language:
<base table="default.lonely"/>
<code language_="python">
<![CDATA[
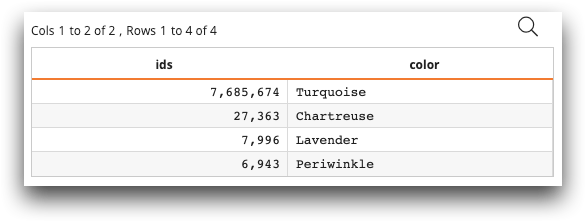
id = np.array([7685674,27363,7996,6943],dtype=np.int32)
col_names = ['Turquoise','Chartreuse','Lavender','Periwinkle']
ops = ten.rebase(pd.DataFrame({'ids':id,'color':col_names}))
]]>
</code>id is a NumPy array containing ids. col_names is a
list containing colors. ten.rebase takes
pd.DataFrame as an argument and returns ops.
ops is a worksheet containing two columns named
ids and color, as shown below:
See Macro Language examples for more advanced examples.
