g_pack(G;S;O;X;N;A)
Returns the bin assignment resulting from applying the specified bin packing algorithm for each value in the given column.
Syntax
g_pack(G;S;O;X;N;A)Input
| Argument | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
G |
any | A space- or comma-separated list of column names Rows are in the same group
if their values for all of the columns listed in If If any of the columns listed in |
S |
integer | The name of a column in which every row evaluates to a 1 or 0, which determines
whether or not that row is selected to be included in the calculation If
If any of the values in
|
O |
integer | A space- or comma-separated list of column names that
determine the row order within a particular group If
If any of the values in |
X |
any numeric type | A column name |
N |
integer | A value that specifies the maximum number of items allowed in each bin Note: The value of the
A parameter (particularly the optional
suffix) determines the behavior in cases of bin overflow. |
A |
text | A value that specifies the heuristic algorithm to use Valid values are:
The default is Each algorithm may optionally
have one of the following suffixes appended to it, which specifies what is to be
done in cases of bin overflow (i.e., when values in X are larger
than the bin size N):
The default in the absence of a suffix is to allow for oversized bins
when necessary (i.e., the same behavior as the |
Return Value
For every row in each group defined by G (and for those rows where
S=1, if specified), g_pack
returns an integer value corresponding to the bin assignment for each value in
X. The heuristic algorithm specified by A computes a
"good" packing of the values in X into bins of size N,
with the optional suffix to A determining the behavior in cases of bin
overflow. The order of the values is determined by the values in O; if
O is omitted, the order is the current display order of the table.
Example
The following example uses g_pack(G;S;O;X;N;A) to divide the contents of
pub.doc.retail.product into bins that have a maximum size of 5000
items. Items that are in the same department will be assigned to the same bin.
<base table="pub.doc.retail.product"/> <link table2="*" col="dept"> <tabu breaks="dept" label="Count of items by department"> <tcol source="dept" name="dept_cnt" fun="cnt"/> </tabu> <willbe name="bin_num" value="g_pack(;;;dept_cnt;5000;)"/> </link>
This example performs a tabulation on the base table to determine the number of items in
each department (dept_cnt). It then specifies that column for the
X parameter to g_pack(G;S;O;X;N;A), the results of which
are saved to the bin_num column. Since the A parameter is
not specified, the behavior of the default algorithm is to allow the bin size to be as large
as necessary over the maximum to accommodate all items in a single department. Since
table2="*" in the <link> operation, the results of
the worksheet associated with the <link> operation are then linked back
into the original worksheet at the point of the <link> (using
table2="*").
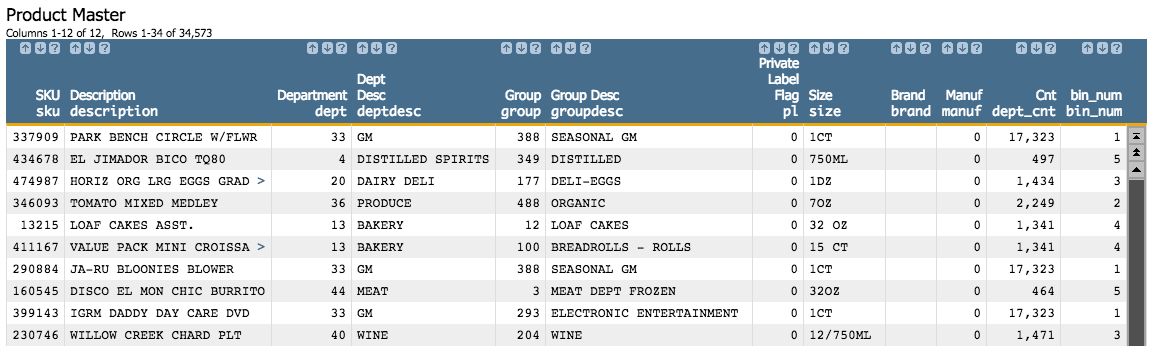
You can see that all items in the dept column that have a value of
33 have a value of 1 in the bin_num
column, which means that all items in department 33 have been assigned to bin number 1. You
can also see that items in department 20 and 40 have a
value of 3 in the bin_num column.
You can see the breakdown more clearly if you look at the results of the worksheet within the link:
<tabu breaks="dept" label="Count of items by department"> <tcol source="dept" fun="cnt" name="dept_cnt"/> </tabu> <willbe name="bin_num" value="g_pack(;;;dept_cnt;5000;)"/>
If you sort the results of the bin_num column in ascending order:
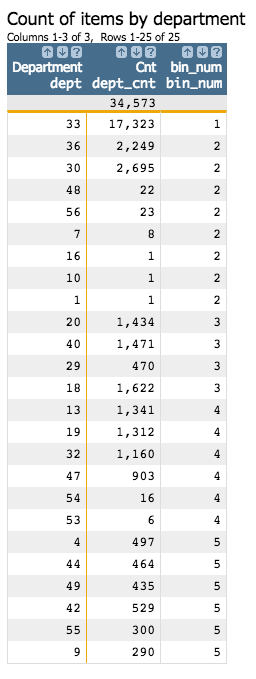
You can see that department 33 has 17,323 items (well over the maximum bin size of 5000, as
specified by the N parameter). All of the other departments have less than
the maximum, so the other bins consist of items from multiple departments. If you do a
tabulation on these results, you can see the distribution among the five bins.
<tabu label="Total items per bin" breaks="bin_num"> <break col="bin_num" sort="up"/> <tcol source="dept_cnt" fun="sum" label="Sum of`Cnt"/> </tabu>
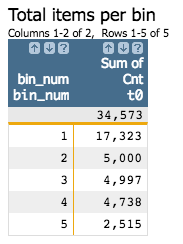
Notice that none of the bins other than 1 have more items than the maximum.
A parameter to g_pack(G;S;O;X;N;A) was
explicitly specified as 'ffd-', those rows with a value of
33 in the dept column would be assigned an N/A value
in the resultant bin_num column. If the A parameter was
explicitly specified as 'ffd0', an error message would be
displayed.