interp(V;N;X;Y;E)
Returns a particular interpolation of a given value based on a discrete set of data points, and if specified, extrapolates out-of-range values.
Syntax
interp(V;N;X;Y;E)Input
| Argument | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
V |
integer or decimal | V is a column containing the values you wish to interpolate.A column name |
N |
integer | Determines the type of interpolation to performN must be
one of the following:
|
X |
integer or decimal | X is any type of value or a list of numbers in a set you wish to
interpolate.
A space- or comma-separated list of scalar values |
Y |
integer or decimal | Y is a list of numbers in a set you wish to interpolate.A space- or comma-separated list of scalar values |
E |
integer | A value of 1 or 0 that determines
whether or not to extrapolate out-of-range values
Note: Extrapolation of higher-order splines is not typically meaningful.
|
X and Y must be space- or comma-separated lists of
equal length.Return Value
Returns a decimal number corresponding to the interpolation of V using the
method specified by N and the values specified by X and
Y.
If E=1, out-of-range values will be extrapolated.
If E is 0 and V is less than the
lowest value in X or greater than the highest value in X,
the result is N/A.
If V is N/A, the result is N/A.
Example
<table> op to create a temporary table to
help illustrate the use of
interp(V;N;X;Y;E):<table title="interp Example" cols="values" types="f">
2.5;
6;
8;
-2.5;
-100;
</table>We'll use the values column from this table for our V
parameter.
For X, we'll use the following list of values:
0,1,2,3,4,5,6 (note that this can be a space- or comma-separated
list).
For Y, we'll use the following list of values:
0,0.8415,0.9093,0.1411,-0.7568,-0.9589,-0.2794 (note that this can
be a space- or comma-separated list).
interp(V;N;X;Y;E) to
interpolate the values in V based on the values in X and
Y. We specify the type of interpolation using the N
parameter and whether or not to extrapolate out-of-range values using the E
parameter:<willbe name="simple" value="interp(values;0;0 1 2 3 4 5 6;0 0.8415 0.9093 0.1411 -0.7568 -0.9589 -0.2794;0)"/>
<willbe name="simple_ex" value="interp(values;0;0 1 2 3 4 5 6;0 0.8415 0.9093 0.1411 -0.7568 -0.9589 -0.2794;1)"/>
<willbe name="linear" value="interp(values;1;0,1,2,3,4,5,6;0,0.8415,0.9093,0.1411,-0.7568,-0.9589,-0.2794;0)"/>
<willbe name="linear_ex" value="interp(values;1;0,1,2,3,4,5,6;0,0.8415,0.9093,0.1411,-0.7568,-0.9589,-0.2794;1)"/>
<willbe name="quadratic" value="interp(values;2;0,1,2,3,4,5,6;0,0.8415,0.9093,0.1411,-0.7568,-0.9589,-0.2794;0)"/>
<willbe name="quadratic_ex" value="interp(values;2;0,1,2,3,4,5,6;0,0.8415,0.9093,0.1411,-0.7568,-0.9589,-0.2794;1)"/>
<willbe name="cubic" value="interp(values;3;0,1,2,3,4,5,6;0,0.8415,0.9093,0.1411,-0.7568,-0.9589,-0.2794;0)"/>
<willbe name="cubic_ex" value="interp(values;3;0,1,2,3,4,5,6;0,0.8415,0.9093,0.1411,-0.7568,-0.9589,-0.2794;1)"/>This will give us the following results:
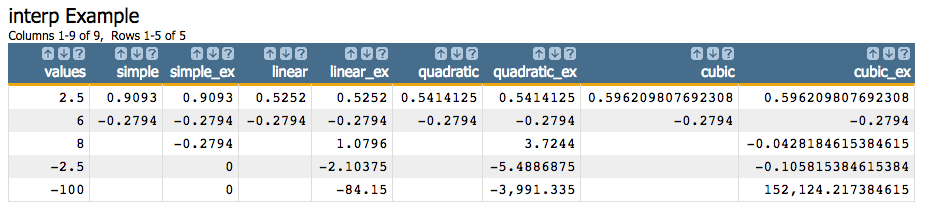
For those rows in the values column that are in the range of
X (i.e., 2.5 and 6), the
interpolated results are returned and are the same regardless of whether extrapolation has
been specified or not.
For those values outside the range of X, the result is N/A in the
simple, linear, quadratic, and
cubic columns, since the E parameter is
0 for those columns. For the simple_ex,
linear_ex, quadratic_ex, and cubic_ex
columns, extrapolation is done since the E parameter is
1.
