new
New spawns a new instance of a QuickApp.
Description
When you use new to spawn an instance of a QuickApp, the API assigns
a unique number to the QuickApp instance, called a tag. The tag number appears in
the URL and in the user interface. The new QuickApp instance has the format
https://[host]/[1010-version]/api/[tag_number].
You also have the option to use queries that don't end with
<dynamic/>. If you do this, the new
endpoint will not add an instid_ attribute to these queries.
Therefore, you must assign your own unique number to the QuickApp instance. You can
make use of the special variable @count for this purpose.
URL
https://[host]/[1010-version]/api/new/[quickapp_name]
This URL spawns a new instance of the QuickApp [quickapp_name].
For example,
https://[host]/[1010-version]/api/new/sql
spawns a new instance of the sql QuickApp.
Alternatively, use the following URL to submit a <dynamic> query
on the fly in the user interface. This is useful for experimenting with a query:
https://[host]/[1010-version]/api/new
Enter the <dynamic> query in the text box and click
Submit.
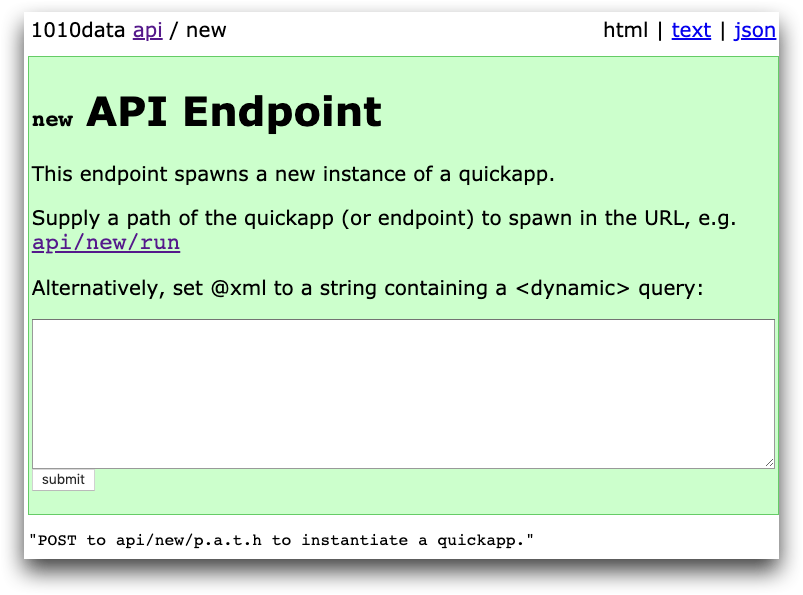
When you successfully spawn a new instance of a QuickApp, the following appears:

Click the link to interact with the new QuickApp instance.
Methods
POST
Parameters
@xml- A string containing a
<dynamic>query.
Response
new returns a numerical tag that enables you to interact with the
QuickApp. To run the QuickApp, use the tag number returned by new in the URL:
https://[host]/[1010-version]/api/[tag_number]
User Interface Example: Spawn an instance of an endpoint
In the following example, the api/new/sql spawns a new instance of
the sql endpoint:

Click the link api/7 to interact with the new sql
QuickApp instance. Interact with the endpoint as you normally would.
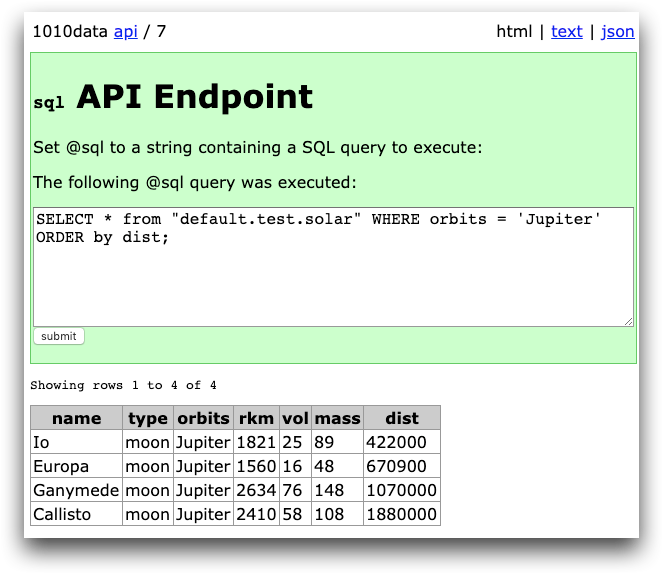
You can return to this instance of the QuickApp at api/7 and
interact with it any time during your session.
User Interface Example: Entering a <dynamic> query
In the following example, a new QuickApp is loaded on the fly using the
@xml parameter in the user interface. @xml
contains a <dynamic> query entered directly into the text box in
the new endpoint.
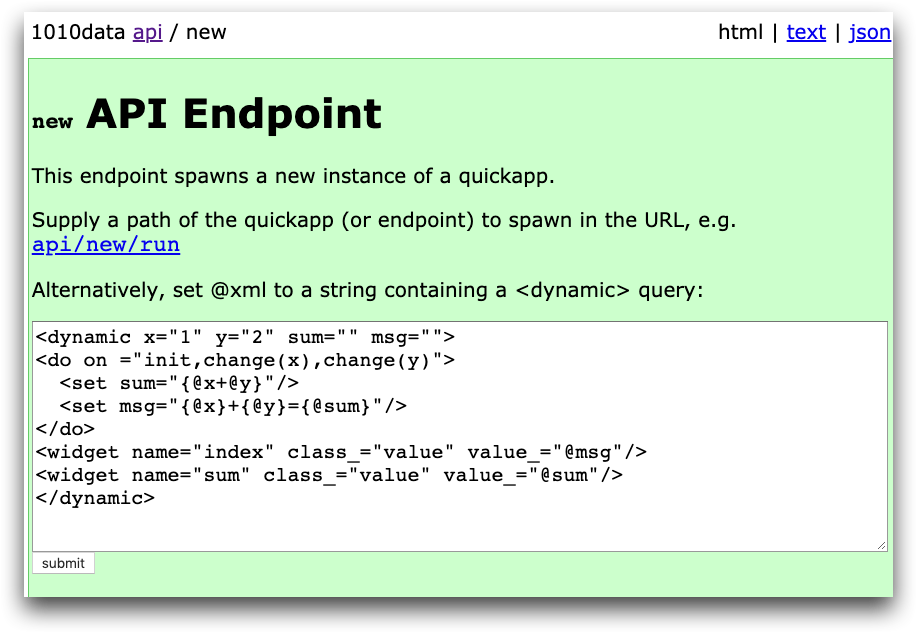
Click Submit to spawn a new QuickApp containing the results of the query. The following screen appears:

Then click the link containing the tag for the QuickApp, in this case,
api/10. The query results appear:

You can also interact with the QuickApp within the URL. In this example QuickApp, you
can change the values of x and y by adding a query
to the end of the URL, such as api/10?x=5&y=7. Now x=5
and y=7. The query results are as follows:

You can return to this QuickApp instance at api/10 and interact with
it at any point during your session.
curl Example: Spawn an instance of a <dynamic> query
You can test a <dynamic> query with curl.
The following is a simple <dynamic> query saved as a file named
app.xml:
<dynamic x="0" y="0" sum="0" msg="">
<do on_="init,change(x),change(y)">
<set sum="{@x + @y}"/>
<set msg="{@x}+{@y}={@sum}"/>
</do>
<widget class_="value" name="index" value_="@msg"/>
<widget class_="value" name="sum" value_="@sum"/>
</dynamic>First, issue a curl command containing the <dynamic> query to the
new endpoint:
$ curl -s -b cookie.txt -d "xml=$(cat app.xml)"
'https://www2.1010data.com/beta-latest/api/new:json'The command returns JSON containing the tag number of the new instance that was created:
{"tag":18}
Then, issue a curl command to the tag that was created:
$ curl -s -b cookie.txt 'https://www2.1010data.com/beta-latest/api/18/:json'This command returns the result of the <dynamic> query as
follows:
"0 0=0,0"
You can also use curl to test different variables in your query, as follows:
$ curl -s -b cookie.txt
'https://www2.1010data.com/beta-latest/api/18/:json?x=5&y=3'The result of the <dynamic> query is now:
"5 3=5,3"
