same(X;Y)
Returns a boolean value indicating whether the two arguments are equal. (Available as of version 11.21)
Syntax
same(X;Y)
Input
| Argument | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
X |
any | The value to compare to Y |
Y |
any | The value to compare to X |
Return Value
Returns a boolean value indicating whether X and Y are
equal. X and Y can be any type, including special values.
Special types (lists, packages, etc.) are compared component to component.
Although X and Y can be different types, values of
different types are never the same. The exception is the comparison of numeric scalars
(e.g., 1, 1.0, and '1'), which is indifferent to type.
Example
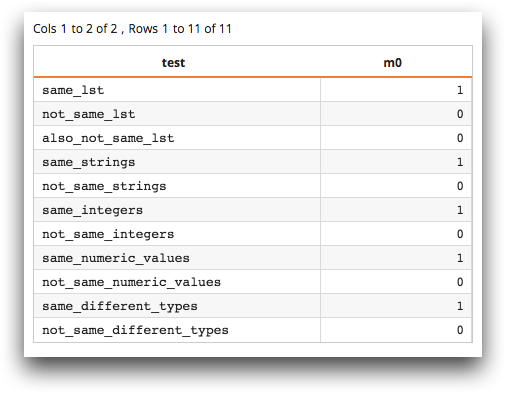
The following example demonstrates the behavior of
same(X;Y) given inputs
of various types.Note: The
<transpose> and <col>
operations at the end of the query are only used to display the results in a more readable
manner for this example and are not germane to the same(X;Y) function in
any way.<table/> <let one_list="{lst('1' '2' '3')}" two_list="{lst('1' '2' '3')}" three_list="{lst('3' '2' '1')}" four_list="{lst('4' '5' '6')}"> <willbe name="same_lst" value="same('{@one_list}';'{@two_list}')"/> <willbe name="not_same_lst" value="same('{@one_list}';'{@three_list}')"/> <willbe name="also_not_same_lst" value="same('{@one_list}';'{@four_list}')"/> <willbe name="same_strings" value="same('foo';'foo')"/> <willbe name="not_same_strings" value="same('foo';'bar')"/> <willbe name="same_integers" value="same(25;25)"/> <willbe name="not_same_integers" value="same(25;50)"/> <willbe name="same_numeric_values" value="same(25;25.0)"/> <willbe name="not_same_numeric_values" value="same(25.0;25.01)"/> <willbe name="same_different_types" value="same(1;'1')"/> <willbe name="not_same_different_types" value="same(1;'2')"/> <transpose namecol="test"/> <col name="test" format="width:25"/> </let>