A cross tabulation provides extra granularity from a summary without losing the
highest level of data summarization.
In this tutorial, you will learn how to perform a cross tabulation to determine the
sales amount by store. The sales totals for each store will be broken out by
department so you can see how much each department contributed to the total
sales.
To perform a cross tabulation:
-
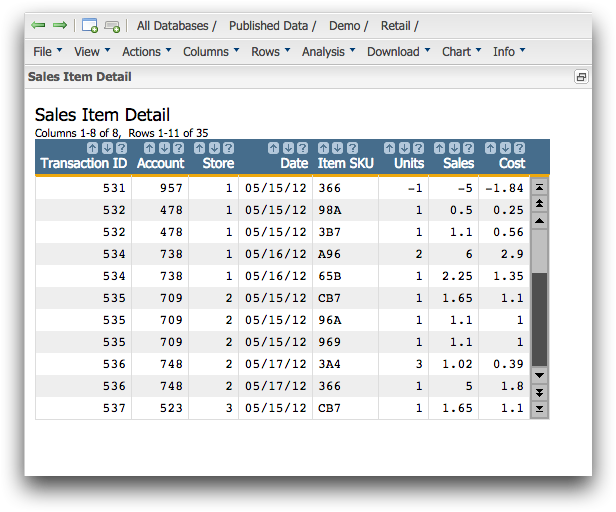
Open the Sales Item Detail table
(pub.demo.retail.item).
1010data displays the
Sales Item Detail
table.
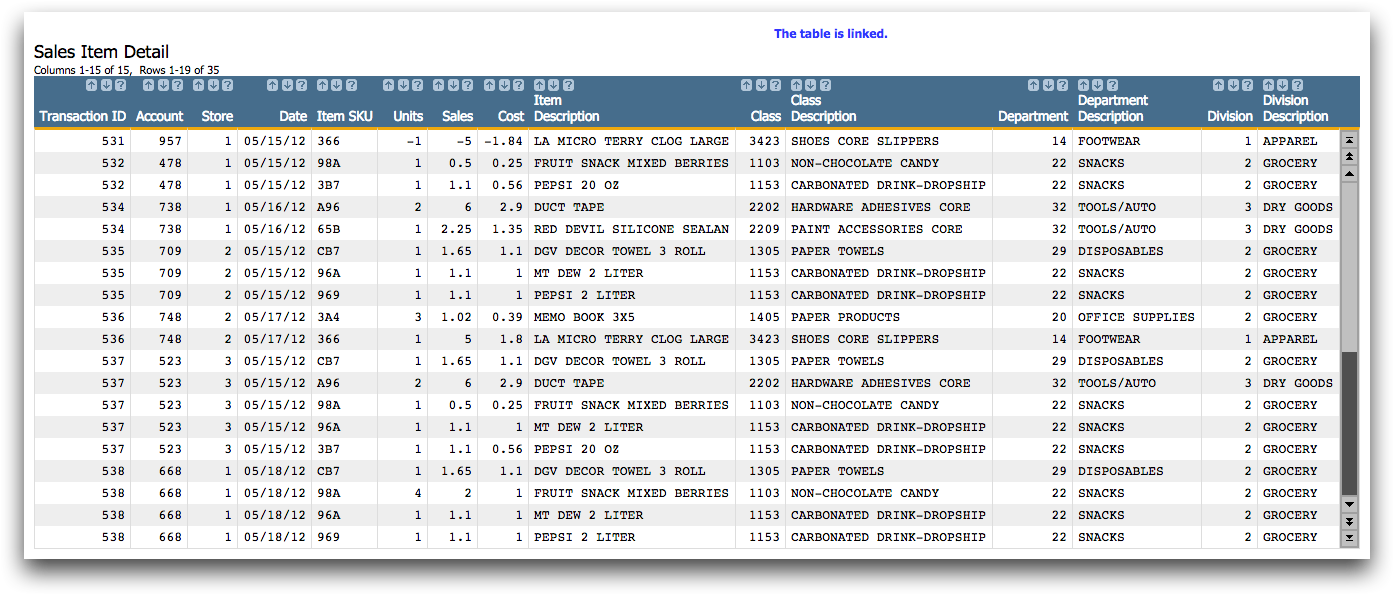
To get the department information for your cross tabulation, you need to
link in the Product Master table. This is identical to the
process used in Link in a table.
-
Click .
1010data displays the Link in Another Table
dialog.
-
Under the Select table section, click the
Product Master table link.
1010data displays the Select columns section in
the dialog.
-
Select Item SKU from the first drop-down list.
-
In the first drop-down list under the Corresponding
Column(s) section, select SKU.
-
In the Suffix field, enter _pm.
-
Click Submit.
1010data links the
Product Master table into the
Sales Item Detail table and displays the results of
the link.
-
Click .
1010data displays the
Cross Tabulation
dialog.
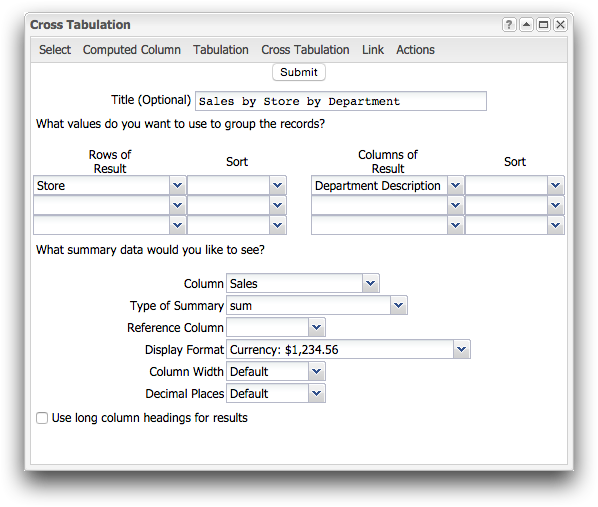
-
Enter Sales by Store by Department in the
Title field.
-
Under the What values do you want to use to group the
records? section, complete the following:
-
In the first drop-down list under Rows of
Result, select Store.
This selection creates a row for each store in the cross
tabulation.
-
In the first drop-down list under Columns of
Result, select Department
Description.
This selection creates a column for each department in the cross
tabulation. The Department Description will be
parsed for its individual values and then summarized. In this case, a
column for each department that had sales will be created.
Next, you need to select the actual summary type. The summary applies to
both the row grouping and the column grouping. In this case, we are calculating
total sales by department for each store.
-
Under the Which summary data would you like to see?
section, complete the following:
| Column |
Select Sales. This selection chooses
the column of data you want to act on. In this instance, you
want to calculate the total sales. |
| Type of Summary |
Select Sum. This selection chooses the
action you want to perform on the selected column. In this case,
you want to summarize the data in the sales
column. |
| Reference Column |
Leave this field blank. |
| Display Format |
Select Currency: $1,234.56. |
| Column Width |
Select Default. |
| Decimal Places |
Select Default. |
-
Click Submit.
1010data displays the results of your cross tabulation.
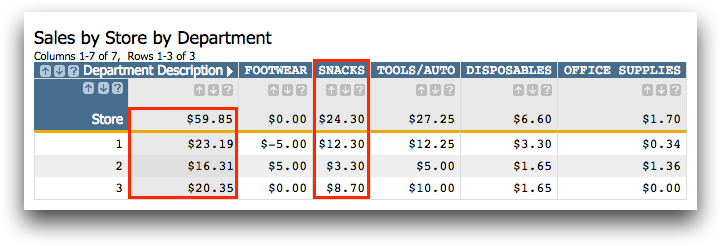
As you can see above, the totals for all the stores are still
available in the first column outlined in red. However, you can also see how
much each department contributed to those totals. For instance, the Snacks
department accounted for $24.30 of the $59.85 in total sales across all the
stores in our fictional retail chain.
Further granularity shows that
in store 1, $12.30 was from the Snacks department.
-
When you are finished with this tutorial, close the Sales Item
Detail worksheet.
Cross tabulations are a great way to get further insight into the numbers of regular
tabulations. You can keep your totals, but see the story behind the numbers by breaking
them down into their constituent parts. Next time you are not sure about why a summary
looks the way it does, rely on a cross tabulation to better understand your data and
your business.





