g_cumhi(G;S;O;X)
Returns the highest value for a given group at the point of the current row being evaluated.
Function type
Vector only
Syntax
g_cumhi(G;S;O;X)
t_cumhi(X)Input
| Argument | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
G |
any | A space- or comma-separated list of column names Rows are in the same group
if their values for all of the columns listed in If If any of the columns listed in |
S |
integer | The name of a column in which every row evaluates to a 1 or 0, which determines
whether or not that row is selected to be included in the calculation If
If any of the values in
|
O |
integer | A space- or comma-separated list of column names that
determine the row order within a particular group If
If any of the values in |
X |
integer or decimal | A column name An N/A in |
Return Value
For every row in each group defined by G and ordered by O
(and for those rows where S=1, if specified),
g_cumhi returns the highest value in the column listed in
X within all rows up to and including that row.
So, for row N, the highest number in column X of group
G will be returned. If, between row N and
N+5, a higher number appears in column X of group
G, that number will be returned for subsequent rows until a higher number
in X appears in group G.
The result is the same data type as X.
If no rows in a group have valid (non-N/A) values for X, the result for every
row of the group is -0I (negative infinity).
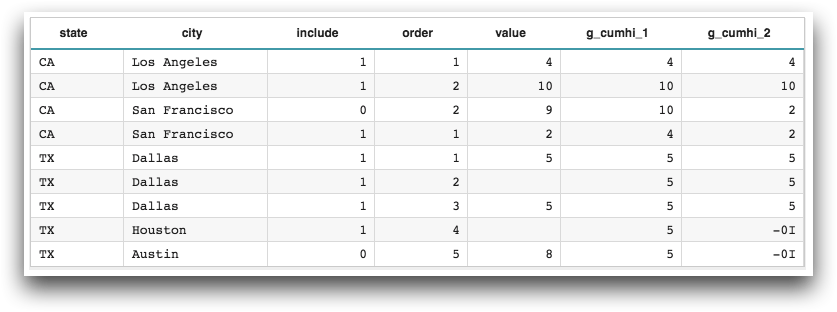
Sample Usage
<base table="pub.doc.samples.ref.func.g_func_time_series_sample_usage"/> <willbe name="g_cumhi_1" value="g_cumhi(state;include;order;value)"/> <willbe name="g_cumhi_2" value="g_cumhi(state city;include;order;value)"/>
Additional Information
- The
t_version of this function defaults theGargument and omits theSargument. The default forGis set at table load time based on the organization of the table.
Example
g_cumhi(G;S;O;X) is an excellent example of the importance of data's
inherent order, and subsequently how to properly use the O argument in
g_functions. In this example, the objective is to find the cumulative high value for the
average temperature in specific zip codes for a given range of dates. There are two ways of
utilizing the inherent order of time-series data to solve this problem, and the method
chosen will change the function call. In the first method, the data can be filtered and
sorted before calling the g_function, in which case the S and
O arguments may be omitted without consequence:
<base table="pub.demo.weather.wunderground.observed_daily"/> <sel value="zipcode=10017,90210,11211"/> <sel value="between(date;20150901;20150930)"/> <colord cols="zipcode,date,meantempi,testhi,testcumhi"/> <sort cols="zipcode,date"/> <willbe name="testcumhi" value="g_cumhi(zipcode;;;meantempi)"/>
However, if pre-sorting by the ordered column and/or filtering the data is not the best
solution, the O argument can be utilized to specify the order of the
evaluation regardless of how the data is sorted. The code below demonstrates how to use the
date column to preserve the order in which the function evaluates
G and X without pre-sorting the data.
<base table="pub.demo.weather.wunderground.observed_daily"/> <willbe name="sargument" value="(zipcode=10017,90210,11211) & (between(date;20150901;20150930))"/> <colord cols="zipcode,date,sargument,meantempi,testhi,testcumhi"/> <willbe name="testcumhi" value="g_cumhi(zipcode;sargument;date;meantempi)"/> <sel value="sargument=1"/>
