g_pick(G;S;O;X;Y)
Returns the value corresponding to a specific position in a particular column within a given group.
Function type
Vector only
Syntax
g_pick(G;S;O;X;Y)
t_pick(X;Y)Input
| Argument | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
G |
any | A space- or comma-separated list of column names Rows are in the same group
if their values for all of the columns listed in If If any of the columns listed in |
S |
integer | The name of a column in which every row evaluates to a 1 or 0, which determines
whether or not that row is selected to be included in the calculation If
If any of the values in
|
O |
integer | A space- or comma-separated list of column names that
determine the row order within a particular group If
If any of the values in |
X |
any simple type | A column name |
Y |
|
The name of a column containing index values The values in |
Return Value
For every row in each group defined by G (and for those rows where
S=1, if specified), g_pick
returns the value of X at index Y where the order is
determined by O. If O is omitted, the order is determined
by the current row order. The result is the same data type as X.
If Y is N/A, less than 1, or greater than the number of rows in the group,
the result is N/A.
Sample Usage
<base table="pub.doc.samples.ref.func.g_pick_sample_usage"/> <willbe name="g_pick_1" value="g_pick(state;include;order;value;index)"/> <willbe name="g_pick_2" value="g_pick(state city;include;order;value;index)"/>
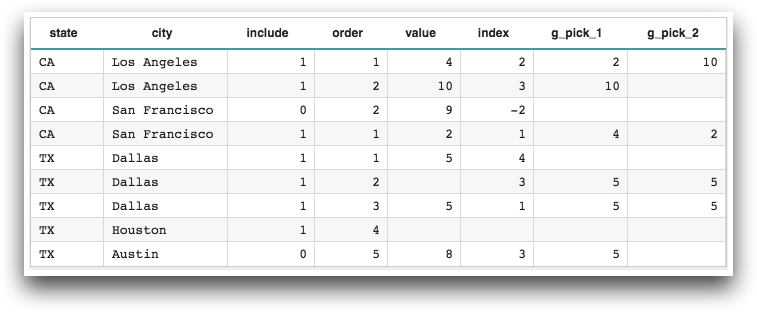
Example
Let's use the Weather Underground Observed Daily table
(pub.demo.weather.wunderground.observed_daily) to illustrate the use
of g_pick(G;S;O;X;Y).
Let's say we want to find out, for each day in every zip code, the first day of the year that the high temperature was five degrees less than the high temperature of that day.
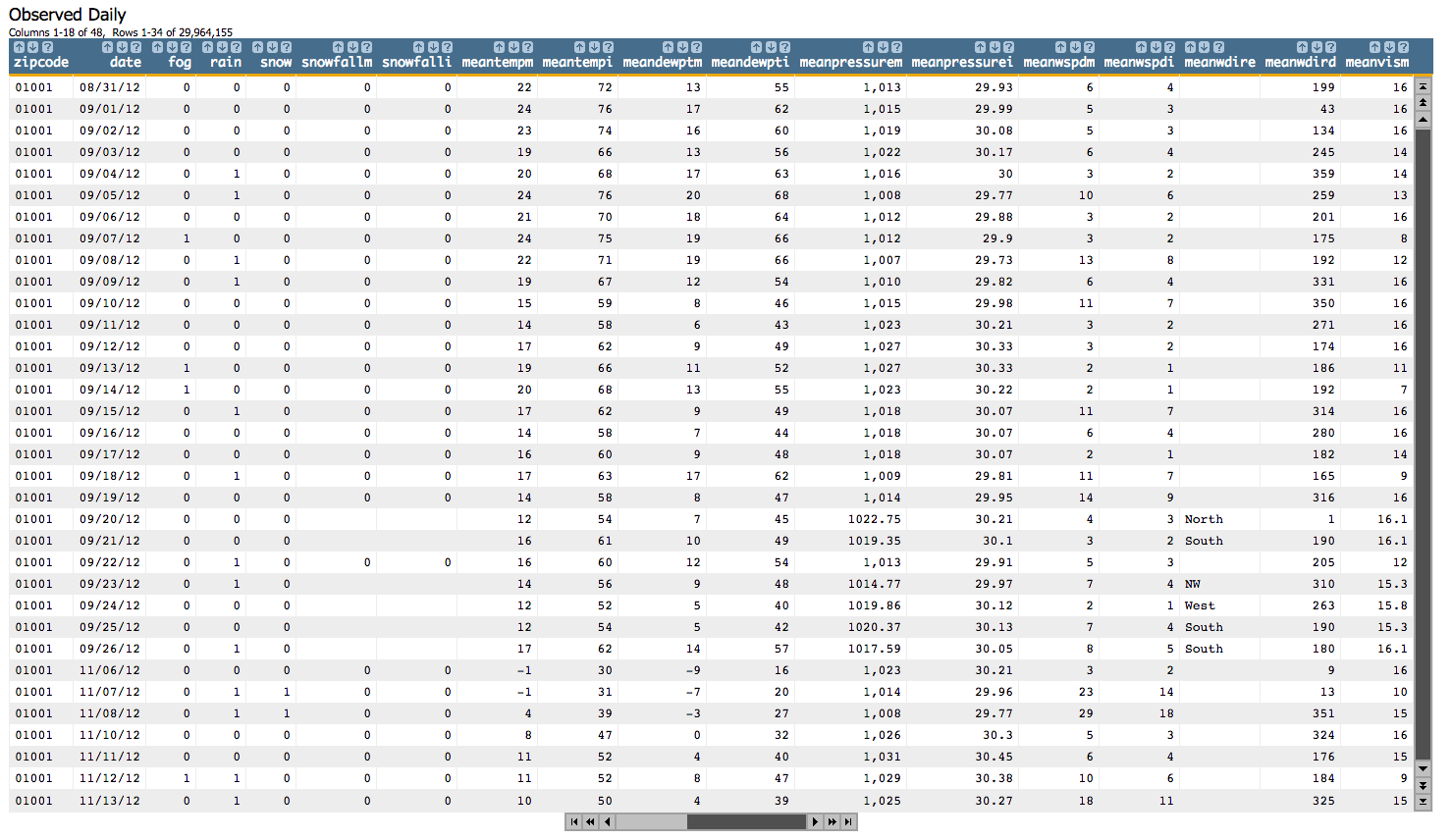
We'll start out by opening the Observed Daily table, which looks something like this:
<sel> operation
and using the year(X)
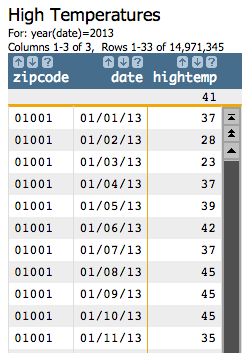
function:<sel value="year(date)=2013"/><tabu>, grouping by both zipcode and
date, and finding the high temperature
(maxtempi).<tabu label="High Temperatures" breaks="zipcode,date">
<tcol source="maxtempi" fun="first" name="hightemp" label="Highest`Max`Temp`(F)"/>
</tabu>fun="first" will give us that high temperature, though we could have
also specified last, lo, or hi for the
fun attribute to get the same results.Our table now looks similar to the following:
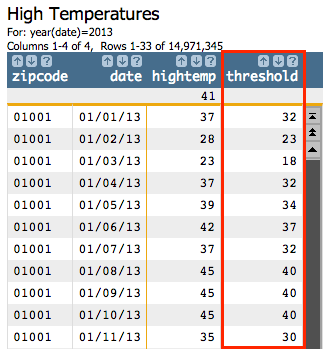
<willbe name="threshold" value="hightemp-5"/>This will give us a new column named threshold:
Now let's use g_position(G;S;O;X;Y) to find the first day of the year that
the temperature was equal to our threshold. Since we want to group by zip code, we'll
specify the zipcode column for our G parameter. We'll omit
the S parameter, since we want the function to consider all rows and not
just a subset. We'll specify the date column for the O
parameter, so that our function considers the order by the date. Since we want to find the
first value in the hightemp column, we'll specify that for
X, and since we want to find the first value in that column equal to our
threshold, we'll specify the threshold column for Y.
<willbe name="day_of_year" value="g_position(zipcode;;date;hightemp;threshold)"/>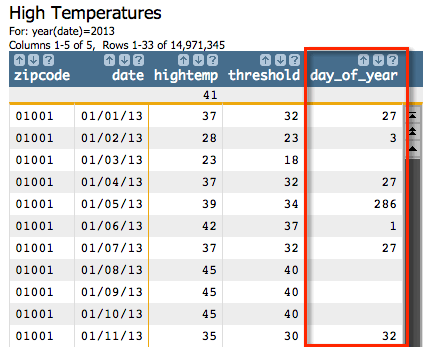
We can see here that for the zip code 01001, the first day of the year that had a temperature that was five degrees less than the high temperature on 01/02/13 (28) was the 3rd day of the year (01/01/13), whose temperature was 23 degrees. If we look at 01/06/13, we can see that the first day of the year that had that a temperature that was five degrees less than the high temperature that day (42) was the 1st day of the year, whose temperature was 37.
g_pick(G;S;O;X;Y) function and give it the
index that we received from g_position(G;S;O;X;Y). Since we want the date
associated with the index, we'll specify the date column for
X, and we'll specify our day_of_year index for the
Y
parameter:<willbe name="first_date" value="g_pick(zipcode;;date;date;day_of_year)"/>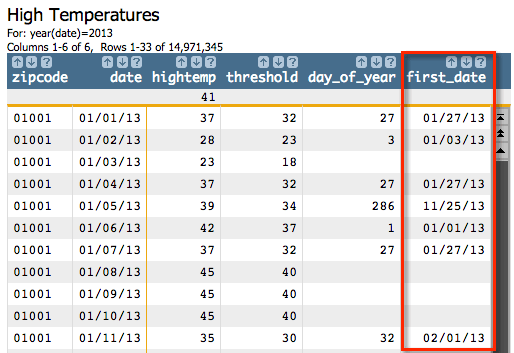
Additional Information
- The
t_version of this function defaults theGargument and omits theSargument. The default forGis set at table load time based on the organization of the table.
