g_ntile(G;S;O;X;N)
Returns an integer representing the quantile interval (or "bucket") for each row that is a member of a given group based on the values in a particular column. Resultant buckets are of roughly equal size.
Function type
Vector only
Syntax
g_ntile(G;S;O;X;N)
Input
| Argument | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
G |
any | A space- or comma-separated list of column names Rows are in the same group
if their values for all of the columns listed in If If any of the columns listed in |
S |
integer | The name of a column in which every row evaluates to a 1 or 0, which determines
whether or not that row is selected to be included in the calculation If
If any of the values in
|
O |
integer or decimal | A space- or comma-separated list of column names that determine the row order within a particular group |
X |
any numeric type | A column name |
N |
integer | The number of buckets to create for each unique value in group
G |
Return Value
For every unique value in the grouping column (G), and for those rows
where S=1, if specified,
g_ntile(G;S;O;X;N) returns an integer representing the bucket into which
each row has been placed, based on values found in column X.
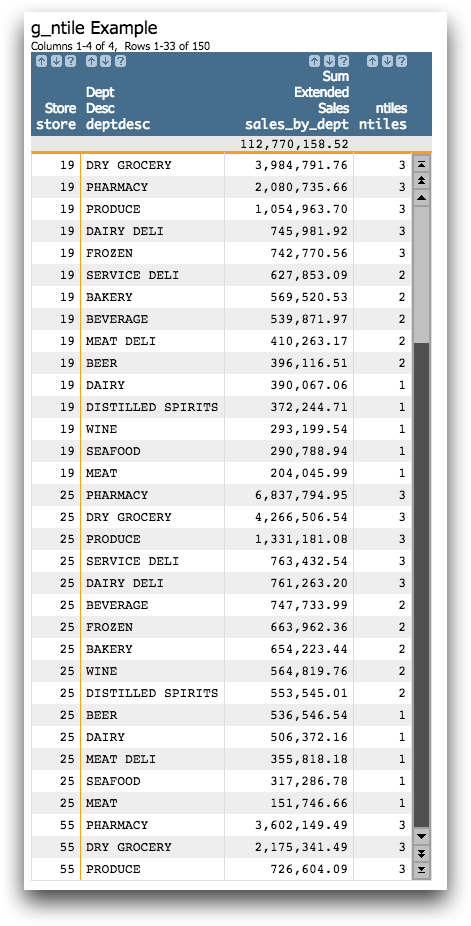
Example
In this example, g_ntile(G;S;O;X;N) provides
a bucket value for each department within a group of stores based on the total sales for
that
department.
<base table="pub.doc.retail.altseg.sales_detail_transid"/> <tabu breaks="store,dept" label="g_ntile Example"> <tcol fun="sum" name="sales_by_dept" source="xsales"/> </tabu> <link table2="pub.doc.retail.altseg.products" col="dept" col2="dept"/> <colord cols="store,deptdesc,sales_by_dept"/> <sort cols="store,`sales_by_dept"/> <willbe name="ntiles" value="g_ntile(store;;;sales_by_dept;3)"/>
The query above returns the following results:
Example: Creating percentiles
N parameter the value 100. In this
example, a tabulation is used to summarize total sales per transaction. A
percentile column is then created using
g_ntile(G;S;O;X;N), indicating which percentile each transaction falls
into vs. the entire
population:<base table="pub.doc.retail.salesdetail"/> <tabu breaks="transid" label="Tabulation"> <tcol source="xsales" fun="sum"/> </tabu> <willbe name="percentile_to_tenth" value="g_ntile(;;;sales_by_transaction;100)"/>
N parameter and divide the
output of the function by
10:<base table="pub.doc.retail.salesdetail"/> <tabu breaks="transid" label="Tabulation"> <tcol source="xsales" fun="sum" name="sales_by_transaction" label="Sales by`Transaction"/> </tabu> <willbe name="percentile_to_tenth" value="g_ntile(;;;sales_by_transaction;1000)/10"/>
Additional Information
g_ntile(G;S;O;X;N):- When there is a "tie" between two values, the value appearing first in the original
order of the data, or the value appearing first in ordered specified with the
Oargument, will be used - Quantiles themselves (e.g., the "dividing line" between buckets, may or may not be values found in the set of rows being broken into buckets
- The lowest numbers appear in the lowest bucket, and the highest numbers appear in the highest bucket
g_ntileis defined as follows:g_ntile(G;S;O;X;N) == int(-floor(-N*((1+g_cnt(G;S)-g_rank(G;S;O;X))/g_cnt(G;S))))
