<def_gfun>
<def_gfun> may be used to define new g_functions in the MDB
expression language. (Available as of version 12.20)
Syntax
<def_gfun name="[NAME_OF_GFUNCTION]"
mode="summary|group|vector"
args="[ARG_NAME1];[ARG_NAME2];...[ARG_NAMEn]"
types="[RETURN_DATA_TYPE]([DATA_TYPE1];[DATA_TYPE2];...[DATA_TYPEn])"
ordered="0|1">
<code language_="[LANGUAGE]">
[CONTENTS_OF_GFUNCTION]
</code>
</def_gfun>
Attributes
name- The name of the
<def_gfun>.The name must begin with an alphabetic character and consist only of alphanumeric characters, digits, and/or underscores. In addition, the name must be unique; that is, no other block in the macro may have the same name.
mode- The mode of the g_function.
Valid values are:
summary- The g_function is passed vectors, once for each group, and should return a
scalar. There is one result value per group. This mode may be used with either
ordered=0orordered=1. This is the default value. group- The g_function is passed ordered vectors, once for each group, as well as a
selection vector, and should return an equal-length vector. This mode may be used
only with
ordered="1". vector- The g_function is passed grouped/ordered vectors, one for each argument, as well
as a class vector and a section vector, and should return an equal-length vector.
This mode may be used with either
ordered=0orordered=1.
args- Specifies the name(s) of the argument(s) in the new g_function.
types- Specifies the return data type of the new g_function and each of the argument data
types in parentheses. If there is more than one possible combination of return types and
argument types, they are separated by a |.
The following are the valid values of
types:s- A string value
f- A floating-point value
i- An integer value
j- A big integer value
n- Any data type
d- A package/model
eLn(orLn,Li,Lf,Lj,Ls)eis an expression andLis a list of a given data type. For example,Lnis a list of columns of any type, such as'store,price,description'.
ordered- Specifies whether the new g_function takes an order (third) argument. The default
value is
0(unordered).
Example: JSON list g_function (defined in Python)
In the following, example, we define a g_function called g_json_listvals
in Python. g_json_listvals creates a dictionary of values for each group.
The g_json_listvals function uses a mode of summary (the
default), takes two arguments, keys and vals, and returns
a string of JSON. By using n as input types, we are allowing arbitrary
input types for the columns, but the results column must be a string (or byte string). The
Python code within [CDATA] defines what g_json_listvals
does. To retrieve values from our dictionary, we define get_json_listvals.
This function retrieves a particular value from the list of JSON values for a given key and
index. If the key or index do not exist, we return NA. In our example, the
<willbe> column dictlist contains the complete
dictionary for the state group. The <willbe> column
val contains the value for "tape" at index position 1.
<library>
<def_gfun name="g_json_listvals" args="keys,vals" types="s(n;n)">
<code language_="python"><![CDATA[
import json
dd = {}
for k,v in zip(keys,vals):
if k in dd.keys():
dd[k].append(v)
else:
dd[k] = [v]
r = json.dumps(dd)
]]></code>
</def_gfun>
<def_ufun name="get_json_listvals" args="listofjsons,key,index" types="s(s;s;i)">
<code language_="python"><![CDATA[
import json
r = []
for j in listofjsons:
pyd = json.loads(j)
if key in pyd:
if index < len(pyd[key]):
r.append(pyd[key][index])
else:
r.append(None)
else:
r.append(None)
]]></code>
</def_ufun>
</library>
<table cols="state,type,size">ca,tape,small
ca,tape,small
ca,tape,large
ca,glue,xlarge
ca,powder,medium
ca,glue,medium
ca,tape,xxlarge
ca,tape,small
tx,tape,tiny
tx,tape,micro
tx,powder,large
tx,tape,xxlarge
tx,glue,small
tx,glue,small
ny,powder,tall
ny,tape,wide
ny,powder,tall
ny,glue,small
ny,glue,small
</table>
<willbe name="dictlist" value="g_json_listvals(state;;type;size)"/>
<sel value="g_first1(state;;)"/>
<colord cols="state,dictlist"/>
<willbe name="val" value="get_json_listvals(dictlist;'tape';1)"/>The result of this code is as follows:
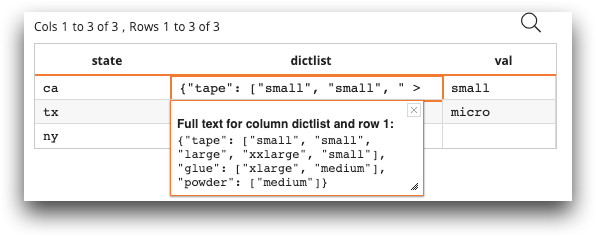
The dictlist column contains the type and
size columns of the state group of the table as JSON.
The val column contains the value of "tape" at index 1. In the case of ny,
there is no value for "tape" at index 1, so it has a value of NA.
