<def_ufun>
<def_ufun> may be used to define new user functions in the MDB
expression language. (Available as of version 12.19)
Description
Functions defined in <def_ufun> in a particular language are global to
the entire session. Once a function has been defined by importing or submitting the library
containing <def_ufun>, it may not be given a new definition without
first clearing the cache. If you attempt to redefine a function, the code will throw an
error. However, you may define a function multiple times with the same definition, meaning
that you can import libraries containing <def_ufun> multiple times
without throwing an error. <def_ufun> should contain a
<code> tag containing function source code.
Syntax
<def_ufun name="[NAME_OF_FUNCTION]"
mode="vector|scalar|raw"
args="[ARG_NAME1];[ARG_NAME2];...[ARG_NAMEn]"
types="[RETURN_DATA_TYPE]([DATA_TYPE1];[DATA_TYPE2];...[DATA_TYPEn])">
<code language_="[LANGUAGE]">
[CONTENTS_OF_FUNCTION]
</code>
</def_ufun>
Attributes
name- The name of the
<def_ufun>.The name must begin with an alphabetic character and consist only of alphanumeric characters, digits, and/or underscores. In addition, the name must be unique; that is, no other block in the macro may have the same name.
mode- The mode of the function.
Valid values are:
vector- The
ufun's code should specify a vector function of all vector arguments. This is the default. scalar- The
ufun's code should specify a scalar function of all scalar arguments, and when the function is passed vectors, it will be executed for each row independently. raw- Arguments are passed to the code as they appear in the invocation: scalars remain scalars and vectors remain vectors.
args- Specifies the name of the argument in the new function.
types- Specifies the return data type of the new function and each of the argument data types
in parentheses. If there is more than one possible combination of return types and
argument types, they are separated by the pipe character (|).
The following are the valid values of
types:s- A string value
f- A floating-point value
i- An integer value
j- A big integer value
n- Any data type
d- A package/model
eLn(orLn,Li,Lf,Lj,Ls)eis an expression andLis a list of a given data type. For example,Lnis a list of columns of any type, such as'store,price,description'.
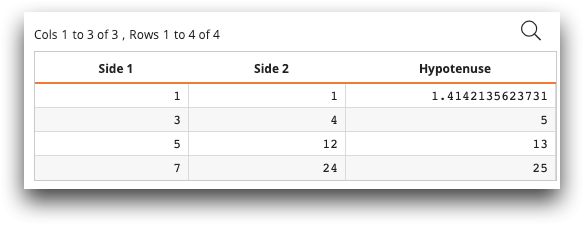
Example: Pythagorean theorem function (defined in K)
In the following example, <def_ufun> defines a function called "pythag"
in K. The function takes two arguments, x and y, (the
sides of a right triangle) and returns a floating-point value (the hypotenuse).
x and y can be integers or floating-point values, and
are supplied as vectors when the function is called on column expressions. Then the Macro
Language code uses the new function pythag to create a new column called
Hypotenuse:
<library> <def_ufun name="pythag" mode="vector" args="x;y" types="f(if;if)"> <code language_="k3"> r:_sqrt(x*x)+y*y </code> </def_ufun> </library> <table labels="Side 1, Side 2" >1 1;3 4;5 12;7 24 </table> <willbe name="Hypotenuse" value="pythag(c1;c2)"/>
The resulting table looks like the following:
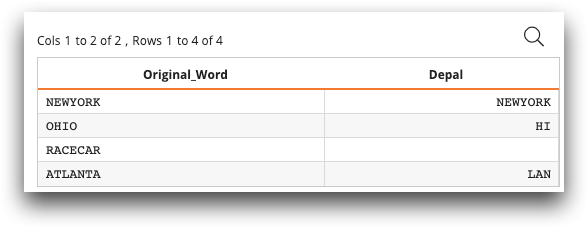
Example: Depalindrate function (defined in K)
In the following
example, <def_ufun> defines a function called "depalindrate" that
returns a different data type depending on the a argument. The function
strips away any characters that are identical reading forward and backward. "depalindrate"
accepts a string, integer, or big integer, and returns the corresponding data
type:
<library> <def_ufun name="depalindrate" args="a" types="s(s)|i(i)|j(j)"> <code language_="k3"> f:{(-i)_(i:(x=|x)?0)_ x:$x} r:f'a r::[-4=4:a;`$r;-1=4:a;0$r;-64=4:a;0j$r;r] </code> </def_ufun> </library> <table labels="Original_Word"> "NEWYORK";"OHIO";"RACECAR";"ATLANTA" </table> <willbe name="Depal" value="depalindrate(c1)"/>The resulting table looks like the following: